Water Quality tests Results: 1970 to 2020 Analysis
- By David Clark
- LSFX Water Quality Test Results: 1970 to 2020 Analysis
- overview
- 2020’s assessment of Lac St Francois Xavier
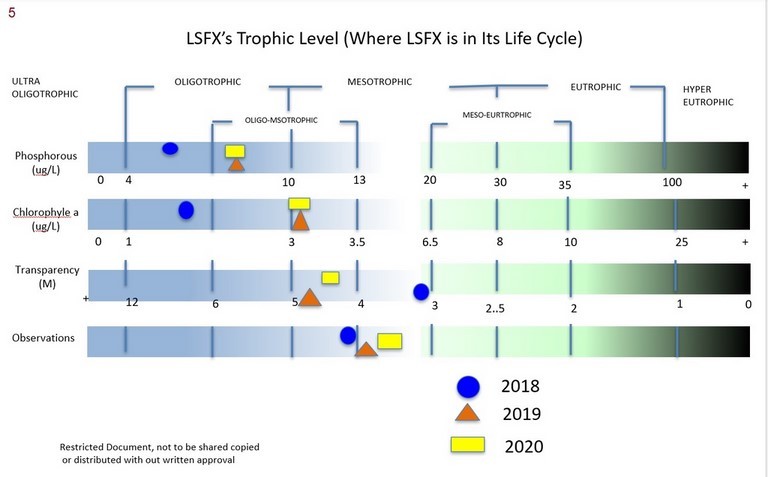
- LSFX’s Trophic Level (Where LSFX is in Its Life Cycle)
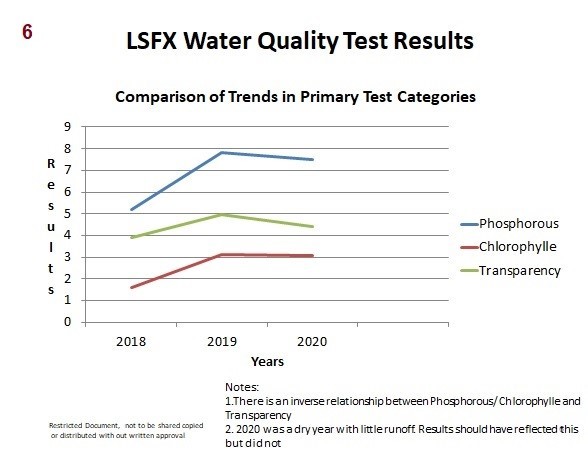
- Comparison of Trends in Primary Test Categories
- Observations About The Lake( base on 70+ years of living on the Lake)
- Factors Influencing Lake Resilience
- A Synopsis Of The Individual Tests
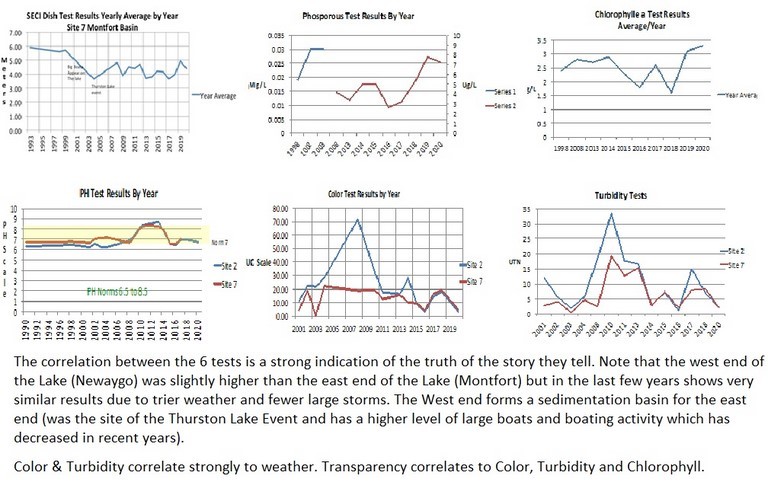
- A Comparison of the 6 Key Test Results
- tests, Risks & priorities
- The Path Forward
- Conclusions
- Priorities
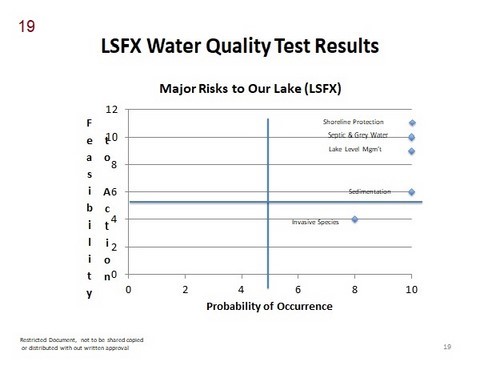
- Major risks to our lake (LSFX)
- Septic and Grey Water: Fecal Coliform
- Sedimentation & Re-sedimentation
- lake level & shoreline
- A Critical Choice
- the details
- The Goal
- Key Points
- Two Hypothesis Behind My Thinking
- Key Success Factors
- An Important Question:
- What factors influence the uniqueness of LSFX?
- Key Events with potential to impact the Lake
- The Tests covered in this Analysis
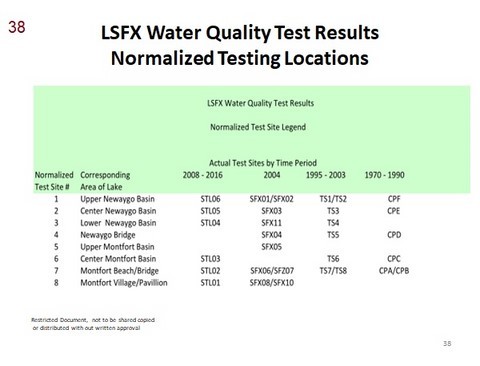
- 38 - Normalized testing locations
- Normalized Testing Locations (map)
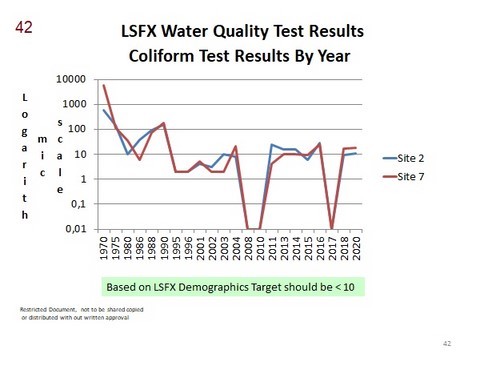
- Fecal Coliform Test Results
- Fecal Coliform Test Results By Year
- Fecal Coliform Test Results By Year (graph)
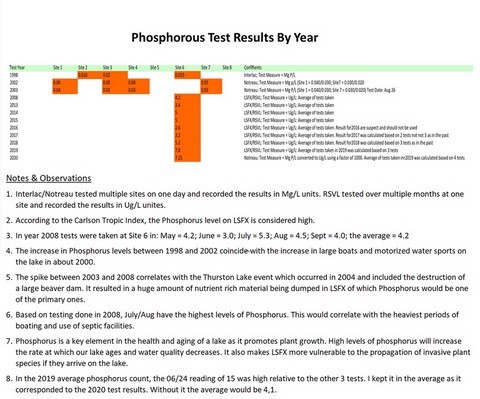
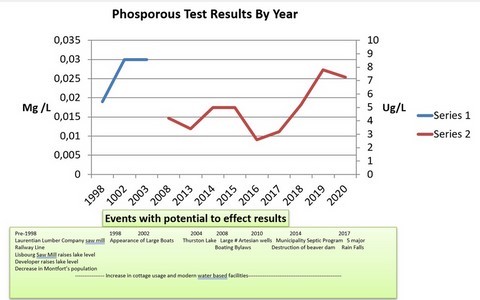
- Phosphorous Test Results By Year
- Phosphorous Test Results By Year (table)
- 45 - Résultats des tests de phosphore, par année (graphique)
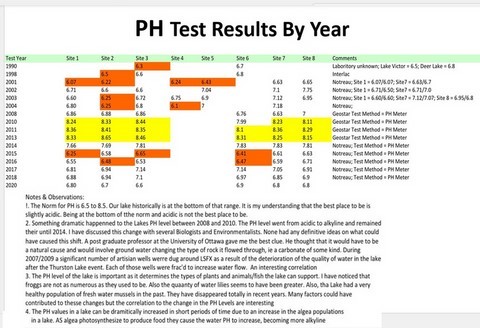
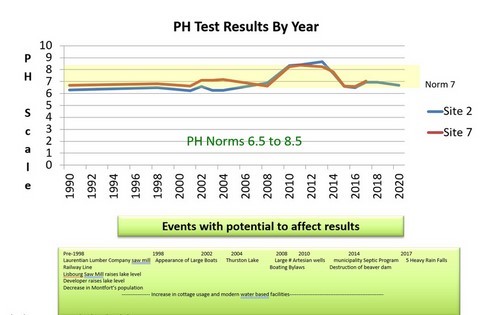
- PH Test Results By Year
- PH Test Results By Year (table)
- PH Test Results By Year (graph)
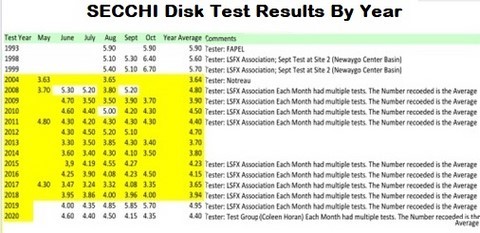
- SECCHI Disk Test Results By Year
- 50a - Secchi disk test results by year, table (1)
- 50b - Secchi Disk Test Results By Year, Table (2)
- 51 - Secchi Disk Test Results Yearly Average by Year (graph)
- 52 - Water Quality Test Results With Secchi Dish
- 53 - Color Test Results By Year
- 54 - Color Test Results By Year, table
- 55 - Color Test Results By Year (graph)
- 56 - Turbidity Test Results By Year
- 57 - Turbidity Test Results By Year (table)
- 58 - Turbidity Test Results By Year (graph)
- 59 - Chlorophyll a Test Results By Year
- 60 - Chlorophyll a Test Results By Year (table)
- 61 - Chlorophyll a Test Results, Average/Year (Graph)
- 62 - Streams – Ammoniacal Nitrogen Test Results By Year
- 63 - Other Tests Conducted (1)
- 64 - Other Tests Conducted (2)
- End
By David Clark
LSFX Water Quality Test Results: 1970 to 2020 Analysis
Prepared By Dave Clark
Restricted Document, not to be shared copied or distributed with out written approval.
overview
IBackground Information
- The Laurentian Lakes were formed at the end of the last Ice Age, About 11,700 years ago
- The life of a lake covers 10’s and possibly 100’s of thousands of years
- The aging process is slow in the early phases and accelerates as it progresses
- The most widely accepted method for determining where a lake is in its life cycle is the Carlson Trophic Index
2020’s assessment of Lac St Francois Xavier
- The lake is healthy
- The Lake is both fragile and resilient. Based on the test results it responses to natural events and how we treat it
- Lac St Francois Xavier is in middle life, in the first half of the Mesotrophic Stage, the transition stage from Oligotrophic (Pristine) to Eutrophic (Old Age) LSFX’s Trophic Level
- The trends that are emerging from the Testing Results indicate a growing stress on the lake and predict an acceleration in its life cycle
Observations About The Lake
( base on 70+ years of living on the Lake)
- The fish population has decreased dramatically and changed in species
- Frogs and other amphibians have decreased in number
- Fresh water clams have disappeared entirely
- Aquatic plants are more prominent and increasing visibly each year, particularly Water Lilies
- The wildlife on the lake is changing. Mallard ducks and Canadian Geese are beginning to make an appearance These new species feed on plants, not fish
Factors Influencing Lake Resilience
- Lac St Francois Xavier is on average 15 feet deep: negative influence
- The LSFX watershed is enormous in comparison to most lakes. This results is a rapid turn over of water: positive Influence
- The lake experiences frequent, large and rapid changes in its water level: negative Influence
- LSFX sits in a deep valley surrounded by high, very steep mountains with a shallow covering of soil. This results in an increased volume of sediments and nutrient rich water reaching the lake : negative influence
A Synopsis Of The Individual Tests
Fecal Coliform:
- 2020 was an average year based on results
- There was very little rain fall and no big storms in 2020
- This should have resulted in a lower than average Fecal coliform count
- Probable cause of the higher than expected count could be the stress on septic systems caused by a greater than normal number of residents living full time on the lake due to COVID
- The continuous 50 year trend of Fecal Coliform presence indicates LSFX has a septic problem that must be addressed
- Phosphorous:
- Phosphorous has been on the rise for the last 4 years
- Probable cause is water management issues arising from development, cottage renovation , increased cottage occupancy, shoreline erosion and road construction
- Phosphorous is a key factor in the aging of a lake
- Phosphorous levels in our lake are above norms (References: Carlson Tropic Index; PHD Biologist at Notreau)
- PH:
- For the last 3 years, PH levels have been very good
- A healthy lake is slightly acidic
- The trends over the years have been erratic and concerning, reaching levels that approach both upper and lower norm boundaries for a healthy lake
- Input from the Notreau Biologist indicates this might be normal and should be tracked and probable causes identified
- Transparency:
- Transparency has remained relatively staple since the Thurston Lake disaster in 2004 with small ups and downs mostly reflecting weather conditions
- 2020 numbers remain approximately 50% less than pre Thurston Lake despite the rapid turnover in lake water
- 2020 should have recorded better than average transparency readings due to the dry summer and absence of large storms but did not. Probable cause, shoreline erosion, sedimentation and an increase in algea
- 2019 data is inconsistent with both previous years and 2020 with no obvious explanation.
- Color & Turbidity:
- Both Color & Turbidity were good this year reflecting the dry summer with no large storms
- Chlorophylle (algae):
- 2020/2019 were the highest recorded levels of Chlorophylle a since we began testing in1993
- This is reflects the upward trend in Phosphorous and in 2020 the dry summer, the absence of large storms, the high temperatures and the increase in the amount of sunshine
- The Streams:
- This was the first year we tested streams entering our lake. The streams tested were Lac a la Croix, Thurston Lake and Mirror lake. These represent 3 of the largest streams entering our lake
- This was also the first year we tested for Nitrogen (ammoniacal nitrogen).
- We have never tested for Nitrogen in the lake
- The Phosphorous levels in the 3 streams tested were all lower than the Phosphorous levels recorded in the lake. In future years we should extend testing for Nitrogen to the lake as well
- Testing of streams must be combined with same tests on the lake to correlate results and understand the impact of streams
tests, Risks & priorities
The Path Forward
A lake is a complex living system with thousands, possibly millions of components and factors we barely understand
Testing gives us a view, a starting point to gain knowledge
The process going forward
- Analyze the results
- Identify possible influencers and develop theories
- Develop and implement actions plans based on those theories
- Monitor results
- If successful continue
- If not successful, repeat the process
We will not get this right all the time. It is an interactive process. The key is continuity and persistence
Conclusions
Consistency is important if we are to optimize the value of our testing program. At minimum we should standardize: the tests, the Laboratory, the test sites, the number & date of the tests and the unites
Tracking Weather, particularly rain & snow fall is critical to interpreting results
The full suite of tests should be preformed in both the Western and Eastern Basins
Testing should be extended to the streams that feed the lake
The Test Result trends are significant and should be explored and action taken
- LSFX is both Fragile and Resilient
- Test results show it’s health reflect how we treat it
- The trends directly correlate with the major events on the lake over the last 50 years
- Living on a lake is wonderful but it comes with responsibilities
- is telling a story and needs our help and cooperation.
Both septic & grey water systems and invasive species which are current threats require immediate action
Sedimentation is the major risk to the lake over time and must begin to be addressed now
We need to engage professional help to develop a scientifically sound Lake Health Management Plan in which this analysis would be included
Priorities
Based on the test results, there are 5 major areas of risks that need to be explored, acted on and monitored on Lake St Francois Xavier. They are all high priority items and all need immediate attention:
- Invasive Species
- Presence of Fecal Coliform
- Sedimentation/Re-sedimentation
- Lake Level Management
- Shoreline Protection and Regeneration
Major risks to our lake (LSFX)
Invasive Species
1. This Threat has been known for over 20 years
2. There are many potential threats, both Plant and animal
3. Eurasian Water-Milfoil is presently at the top of the list and has invested lakes in our area
4. The propagation of invasive species is primarily a result of human intervention but can also result from natural events such as climate change
5. What is needed:
- A permanent group within the Lake Association that on a yearly basis Identifies threats, assesses risks, establishes priorities, develops action plans and mobilizes the LSFX Watershed Community.
- Membership must include the Watershed Community, the Municipality and have access to government resources. This could be set up as a Municipality wide function under the direction of the Municipality and benefit all lakes
- The full support and active participation of the watershed community in implementing the action plans and monitoring results
The current Eurasian Water-Milfoil crisis is an excellent example of our community’s and municipality’s inability to effectively work together, mobilize and respond
Septic and Grey Water: Fecal Coliform
1. On LSFX the primary cause is septic and grey water systems
2. The result is health risks to the community and an increase in phosphorous entering the lake
- Increased Phosphorous fosters aquatic plant growth including Eurasian Water-Milfoil and Algae
- Represents an important factor in the aging of a lake
3. What is needed:
- Every household must ensure that the septic and grey water systems:
- meet regulations
- Are operating at 100%
- Are cleaned regularly
4. Lack of road access is not an inhibitor for residents to solve this issue
It seems easy but we still have issues in this area
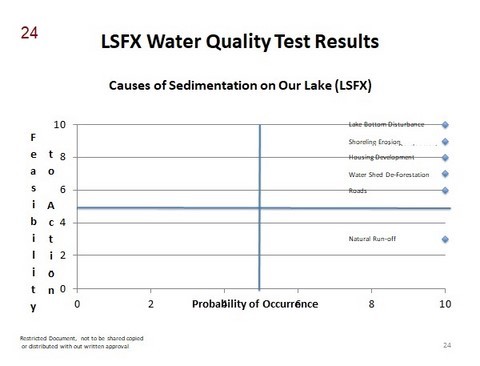
Sedimentation & Re-sedimentation
Sedimentation
The entry of nutrient rich material, such as soils, leaves, wood, etc. into the lake
Effects:
- Nutrients dissolve in the lake’s water. Phosphorous is the primary concern
- The nutrient rich water fosters plant growth which reduces oxygen levels and accelerates the natural aging of the lake
Causes:
- Run off from heavy rains
- Events such as Thurston Lake, Breakage of beaver dams that cause large amounts of sediments & biomass to enter the lake. They have the same & often greater effects than heavy rains
- Shoreline degradation (caused by both nature and Humans)
- Poor drainage due to development and road construction
- Wave action from Boats
What is Needed:
- Restoration of shorelines to prevent erosion and allow plants/trees to absorb the nutrients before they enter the lake
- Prevent any Human related activity that results in sediments entering the lake through a vigilant monitoring of all construction, landscaping, lumbering etc. by both residents and the Municipality
- Minimize the entry of fast running water into the lake by eliminating direct entry, reducing the slope of the flow and creating sedimentation pools if possible.
- Minimize the wake size of boats. The goal could be to contain wake size to the maximum natural wave size on the lake. Go slow and don’t overload
Re-sedimentation
The disturbance of sediments already at the bottom of the lake and turbulence from boats that cause sediments to remain in suspension longer thus releasing larger quantities of nutrients. Sediments at the bottom of the lake release nutrients into the water at a very slow rate as they are not in direct contact with the water and the temperature is lower.
Effects:
- Nutrients dissolve in the lake’s water. Phosphorous is the primary concern
The nutrient rich water fosters plant growth and accelerates the natural aging of the lake.
Causes:
- Wave action from boats at the shorelines
- Jet streams from motors that reach the lake bottom. The lake is on average 15 ft deep and the jet streams go down up to 20+ ft
- Any other action that disturbs the lake bottom
- What is Needed:
(Its not about boats it is about boat operation. Something within our control)
- Leave the shore and docks slowly
- Reduce speed in the shallow parts of the lake
- Reduce Wake size near the shore. On our lake due to its narrowness this would almost be everywhere
lake level & shoreline
Lake Level Management
The problem is not the level of the lake, it is the range of that level.
“The level of LSFX has a range of approximately 24 inches from lowest to highest. Even average, normal rain falls causes the lake to fluctuate 3 to 5 inches in a 24 hour period. Heavy Rains have caused an 18 inch rise in 12 hours”
1. Engage professional expertise to determine the source of the problem and its effect on the lake’s health
2. Work with the Municipality to identify and implement appropriate actions
Shoreline Protection & Regeneration
The causes on LSFX are:
• Wakes from boats
• Deforestation of shorelines
What’s needed:
• Minimize boat wake size
• Don’t overload
• Stay as far from shore as possible
• Regenerate & Naturalize shorelines to prevent erosion
A Critical Choice
We as a community need to make our choices,
Do we respond or not
Each of us must make a choice, do we:
• Remain outside the living system called LSFX and see it as a resource to satisfy our needs and desires
or
• Become part of the LSFX living system and view its protection and health as vital to us, our well being and our continued enjoyment of this beautiful environment
the details
• Test results (in a next presentation)
The Goal
• To increase the Community’s knowledge of the Lake’s environment & evolution by:
Sharing information
Increasing awareness
• To capture your thoughts, views and knowledge and incorporate them into this material:
Extend the scope & depth of the community’s knowledge and awareness
• To provide a basis to come together as a community to take action on the Lake Environment needs
To engage you as an active participant moving forward
• To enlist your help in getting this information out to the community
Key Points
• This is not a scientific study. It is an analysis of test data over time relating trends to events in the watershed
• All test results reflect testing done by qualified, professional, certified laboratories
• The 2020 view has been reviewed by a PHD Biologist from Notreau, our testing lab and her input included
• The test data has been normalized to account for:
Missing years
Changes in test sites
Different laboratories
Variations in unites of measure between laboratories
• The correlations between test result trends and events are not definitive but represent possibilities. This analysis is meant to provide a starting point to explore those possibilities and identify others
• The purpose and value of this analysis is to establish trends over time, relate them to known events and provide a basis for asking questions, enhancing our interaction and management of the watershed and prioritizing actions
• The health of the Lake is primarily a reflection of the health of its Watershed
Two Hypothesis Behind My Thinking
Natural, living systems like our lake ecosystem have boundaries in which they operate that accommodate normal environmental events
They are resilient within their normal operating boundaries
the corollary
When pushed outside their operating boundaries by abnormal events they need help
The response of the environment corresponds directly to the magnitude and severity of an event
Normal environmental conditions and low impact events result in stable test results
the corollary
High impact events and changes result in correspondingly large changes in test results
Key Success Factors
New York State Department Of Sustainable Resources: Diet for a Small Lake)
1. All User/Interest Groups must be involved and must buy into:
1) Results
2) Conclusions
3) Action Plans
2. All aspects of the watershed ecology & use must be open to investigation, analysis & action
3. Action Plans must be measured and modified based on results
An Important Question:
Will the test results from other lakes in the region be applicable to LSFX, our Lake?
• Test results for all lakes will reflect the same elements of the watershed. Some of the more important ones would be:
Geology: topology, structure, mineral content, etc.
Biology: terrestrial, aquatic
Bathometry: size, depth, basin plan, Etc.
Hydro-Cycle: weather, input streams, output Streams, Runoff, etc.
Current environmental condition: shorelines, forested boundaries,
Human footprint: development, roads/railroads, waste treatment, high density housing (i.e. the village), etc.
Usage: industries (i.e. farming, lumbering), boating, eco-tourism, parks, beaches, etc.
History:
• The unique combination of all of these & others will result in each Lake in our Region being unique, i.e. The Nature & Severity of Challenges, Priorities & Action Plans
• In fact the lake will change from year to year as these elements vary
What factors influence the uniqueness of LSFX?
• Geology:
Topology: High steep mountains increase water runoff
Mineral content: high in iron & manganese
Minimal soil coverage with poor water retention over a hard non porous rock
• Bathometry :
Depth: average depth is approximately 5 meters; 2 deep holes, 40 ft. & 60 ft.
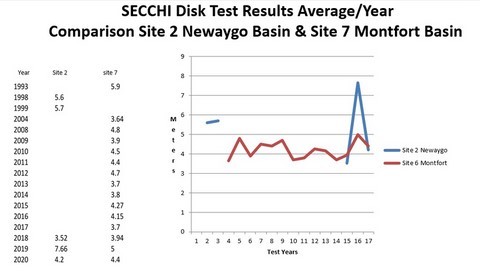
2 basins, Newaygo Basin & Montfort Basin , at different stages in the Lake’s life cycle
The Newaygo Basin has been characterized as a sedimentation basin for the Montfort Basin
The area of the watershed is very large relative to the lake’s basin
• History:
LSFX has been populated for approx. 150 years
The level of LSFX has been changed twice: In the 1920’s & in the 1970/80’s
• Current environment condition:
LSFX ‘S water level has a broad range of 2 ft. or more and responds significantly to even average rain falls
• Human Footprint :
There has been a significant Human footprint on LSFX for 150 years
There are 2 high density housing areas on the lake
LSFX has had a village in the Montfort sector of its watershed for 150 years
• Usage:
CP Rail line traversed almost 50% of our shoreline for 70+ years resulting in shoreline degradation & the creation of the 2 basins from a single lake
The Aerobic corridor and road running beside the lake resulting in continued shoreline degradation
Large lumbering operations resulting in almost 100% deforestation
Laurentian Lumber company: late 1800 through the early 1900
Montfort Orphanage Lumber Mill: 1930’s /1940’s
A major commercial lumber mill in the late 1800’s and early 1900’s. Large quantities of debris on the lake bottom particularly from the Montfort beach to the pavilion
Farming by both the Montfort Orphanage and Founding Families
A popular tourist destination up to the 1950’s, Hotels, boarding houses and day visitors
Motor boats have been on the lake since the 1940’s with numbers and size growing every year
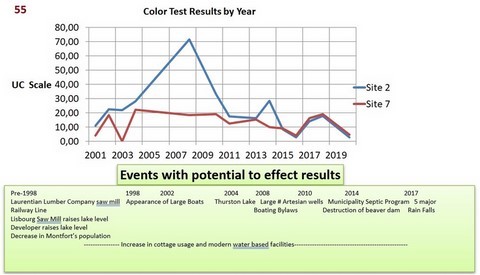
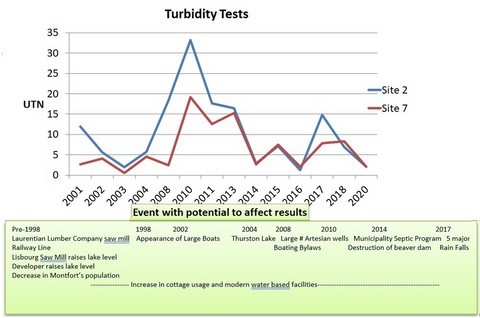
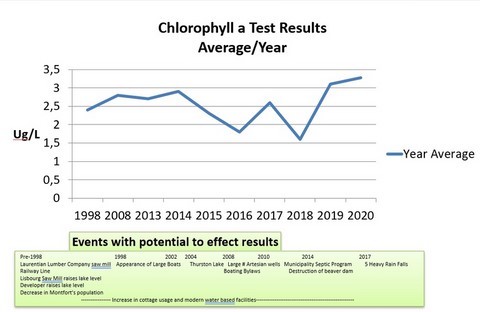
Key Events with potential to impact the Lake
1. Laurentian Lumber Company’s Saw Mill ~1900
2. The Railway line ~1890’s – 1960’s
3. Lisbourg Saw Mill raises lake level ~1930
4. Decrease in the Montfort Population 1950’s
5. Developer raises the Lake Level ~1970’s
6. House in Newaygo falls into lake and must be removed ~2012
7. Appearance of large boats and increased watersports 1998 to present
8. Thurston Lake: January 2004
9. Boating By-Laws go into effect 2008
10. Large number of Artesian Wells 2008 – 2010
11. Municipality focuses on Septic & Grey Water Installations ~ 2010
12. Years of abnormally heavy rain falls 2017
13. Destruction of Beaver Dams ~2014, ????
14. Increase in cottage use and modern water based facilities ongoing
#’s 7 to 12 (Green) can be correlated to Test Results at this time
The Tests covered in this Analysis
Fecal Coliform Test Results
What is Coliform:
It is the bacteria that results from animal and human wastes. It is a indictor that the water might contain health risks. Coliform remains in the water for a short time resulting in tests results reflecting conditions at the time of testing making trends for Coliform test results important.
The Norms are:
Drinking: < 1; Household consumption: < 10; Swimming < 100
Factors that effect Coliform Levels:
- Septic installations not functioning at 100%. e.g: Leaking, not regularly cleaned, do not meet regulations, out of date systems over used, etc.
- Farms/ animal wastes that drain into the lake: Manure piles, Etc.
- Concentrated Wild Animal colonies: eg. Beavers, Geese/ducks, Etc.
- Beaches/High use swimming areas
- The weather: large rainfalls and wet seasons
Phosphorous Test Results By Year
What Is Phosphorous?
It is 1 of 3 key factors in the growth of plants and the one we have the most influence over
The other 2 are temperature and sun light
Nitrogen is another nutrient that influences plant grow. We have begun test Nitrogen this year
The Norms are:
TBD (one source indicated that a 10 % change in Phosphorous Levels is considered significant)
Factors that affect Phosphorous Levels:
• Septic & Grey Water systems
• Ground Water Flow
o Within the bed rock
o Through the soils/earth
o Streams, ditches, poor drainage (roads, housing, landscaping etc.)
• Sedimentation
o Natural Causes:
Steep Slopes
Water Run-off (particularly after Heavy Rains)
• Shoreline erosion
o Removal of natural vegetation
o Wave action from boats
• Re-sedimentation ( the disturbance of sediments on the lake bottom)
o Underwater turbulence from boat Motors ( the bigger the displacement, propeller and drive force the more turbulence)
o Results in sediments remaining suspended in the water and releasing nutrients longer
• Fertilizers
• The decomposition of organic material
PH Test Results By Year
What is PH:
PH is the measure of the Lake’ s acidity level. The scale is algorithmic and is from 0 to 14 with 7 being neutral. Numbers less than 7 indicate the Lake is acidic. Numbers above 7 indicate the Lake is alkaline. PH is important as it determines if a Lake can support life and what kind of plants and fish etc. can survive. It can also indicate an increase in aquatic plants
The Norms are:
6.5 to 8.5 are considered acceptable. A PH of less than 5.5 will not support life. A PH between 5.5 and 6.0 are considered to be in transition, ie. moving from life supporting to dead
Factors that affect PH:
• Acid Rain
• Ground water flow & Composition of the rocks & soils water flows through
• Products that we use that travel to the lake;
o Eg. Cleaners paints,, fertilizers, chlorine/bromine from pools & SPAS, etc.
• Cement
• Exhaust from engines
• Decomposing vegetation, e.g. wood, leaves
• Photosynthesis of Aquatic Plants (Particularly Algae)
SECCHI Disk Test Results By Year
What is the SECCHI Disk Test:
The SECCHI Disk measures the transparency of the water, i.e. How far you can see in the water. It is a measure of the amount of material suspended in the water.
The Norms are:
To my knowledge there are no specific norms for this test. The distance is measured in meters and the larger the number the better the result. Year / Year stability or increasing distance is positive
Factors that affect SECCHI Disk results:
• Water run-off particularly from heavy rains
• Shoreline erosion; large boats, shoreline degradation
• Disturbance of the Lake’s Bottom; large boats, dredging
• Poor drainage; road construction, housing, landscaping, etc.
• Increase in aquatic plant life (e.g. Algae growth)
• Pollen form trees in the spring. Leaves in the fall
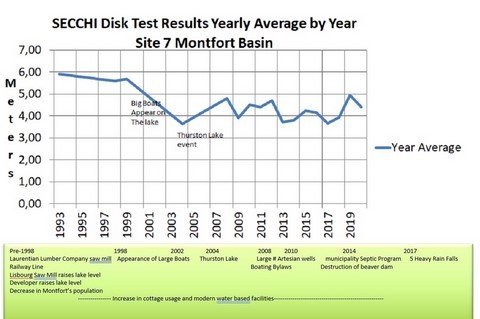
50b - Secchi Disk Test Results By Year, Table (2)
- The beginning of the downward trend between 1993 and 1999 correlates with the appearance of very large boats on the lake and the increase in motorized water sports.
- The significant drop, approximately 50%, in 2004 correlates with the Thurston Lake event which results in a huge amount of organic material entering LSFX.
- It is interesting to note that although the Lake recovered by 2008, it never went back to pre-2004 levels. In the technical studies done as part of the Thurston Lake Class Action, it was predicted that LSFX would return to normal due to the good water flow in the lake. The continued lower level of water clarity is mostlikely the result of the continuous presence of large boats, large wakes and a higher level of motorized watersports on the lake.
- The upward trend in 2009 correlates with the introduction of Boating By-laws. However, the downward trend since then reflects dis-regard of those by-laws.
- Construction and road building have not changed enough to account for the continued decrease in Secchi Disk results.
- Weather patterns, particularly the amount and rate of precipitation, is the factor that affects the quality of our lake the greatest and is aggravated by human activity. 2017 was a very wet year with 4 major downpours.
- This is another indicator of our choices as a community and as individuals.
- 2019 Sept & Oct results were higher than expected and do not line up with previous years or 2020 results. An explanation for this is not obvious.
- 2020 was a dry year with no large rain storms. This resulted in better Secchi Disk results.
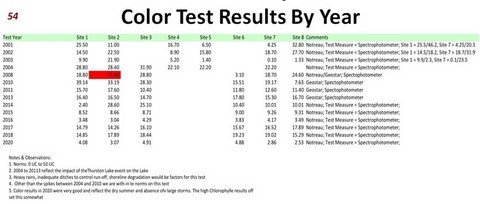
53 - Color Test Results By Year
Water should be colorless. However, natural processes create chemical reactions that give water its color
0 UC’s to 50 UC’s (true color units)
Factors that affect Color:
Chlorophyll a (Algae)
Dissolved minerals, I.e. iron, manganese
Tannin from leaves
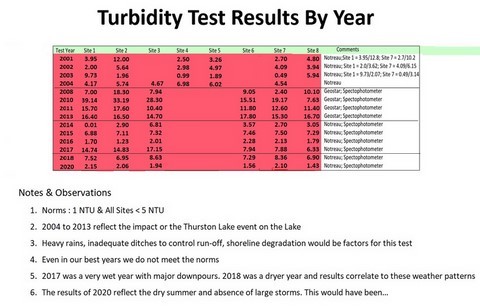
56 - Turbidity Test Results By Year
- Turbidity is the measure of murkiness due to suspended particles in the water.
- Turbidity levels outside the Norms is important as it has a detrimental effect on aquatic organisms
- 1 NTU per site and all sites less than 5 NTU’s
- Water run-off from Heavy rains
- Shoreline erosion; large boats, shoreline degradation
- Disturbance of the Lake’s Bottom; large boats, dredging
- Poor drainage; road construction, housing, landscaping, etc.
- Algae growth
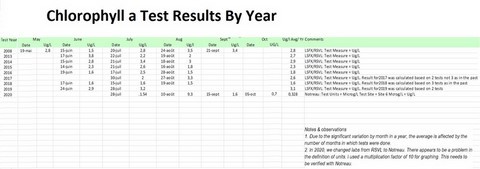
59 - Chlorophyll a Test Results By Year
What is Chlorophyll a:
Chlorophyll a is a measure of the density of the Algae population of a lake.
Chlorophyll a is the pigment that gives a green color to plants.
The Norms are:
TBD
Factors that effect Chlorophyll a:
- Phosphorous & Nitrogen and by extension all factors that affect the phosphorous & nitrogen levels in a lake
- Temperature of the water
- Sun light